22+ Circadian Rhythm In Plants
Web PMC9019581 DOI. Huang and Nusinow 2016.

Role Of Circadian Rhythm In Plant System An Update From Development To Stress Response Sciencedirect
Web The rhythmicities or periodicities whose periods match to those of lunation are called as circalunar rhythms period 29 days to those of tide are called as circatidal rhythms period 124 or 248 hrs to those of seasons are called as circaannual rhythms period a year or to those of time between successive spring-low waters are called.

. Web Although plants have provided many examples of rhythmic outputs and our understanding of photoreceptors of circadian input pathways is well advanced studies with plants have lagged in the identification of components of the central circadian oscillator. Web These Circadian rhythms endogenous rhythms with periods of 24 h driven by an internal circadian clock cause a variety of changes including changes in transcription and post-transcriptional regulation in plants. Web The effect of Ca 2 is through signalling 22.
Chronobiology is the study of circadian rhythms. In plants the clock regulation is based on a set of genes with peak. Web Circadian Rhythms.
Web Circadian rhythm predicts a 24-h cycle with 16 h of light and 8 h of darkness in response to abiotic and biotic factors as well as the appropriate temperature. Web Circadian rhythms in plants articles from across Nature Portfolio. For a plants fitness proper growth and development these rhythms synchronize the diurnal photoperiodic changes.
Web In this review we discuss our current understanding of the circadian clock network and how environmental cues are integrated into this complex regulatory system. Circadian rhythms are physical mental and behavioral changes that follow a 24-hour cycle. Web Circadian rhythms endogenous rhythms with periods of approximately 24 h are widespread in nature.
The rhythms in stomatal conductance were described by Francis Darwin almost 100 years ago. Web This regular repetition of growth or activity on approximately a 24hour cycle is called a circadian rhythm. This review aims to summarize the existing literature on circadian hormonal and sleep rhythms in the oncological population focusing on circadian disruption and physiological and.
All sorts of metabolic processes are circadian such as cell divisions in root tips and protein or hormone synthesis. Web What are circadian rhythms. Hsu and Harmer 2014.
Web Indeed variation in clock genes has been implicated in an array of plant environmental adaptations including growth regulation photoperiodic control of flowering. Notably more data have suggested the circadian clock links chrono-culture to key agronomic traits in crops. Levels of these proteins are in constant flux each peaking at a specific time of day and feeding back to regulate.
Hsu and Harmer 2014. Circadian rhythms are the approximate 24-h activity cycles of various biological processes regulated by an innate circadian clock in almost all. Web THE PLANT CIRCADIAN CLOCK The plant circadian clock is a complex net-work of intertwined feedback loops comprised of repressor and activator transcription factors Harmer 2009.
SUMOylation contributes to timekeeping and temperature compensation of the plant circadian clock. The Focus Collection on Circadian Rhythms addresses topics ranging from the molecular nature of the circadian oscillator to ways in which it influences diverse aspects of plant physiology growth or development. Web The driving force behind circadian rhythms is what scientists call the circadian clocks central oscillator an elaborate network of genes that turn each others activity on and off.
Web In patients with an acute myocardial infarction disrupted circadian rhythms during the initial days in the cardiac intensive care unit caused by factors such as noise excessive night-time light. Web Circadian rhythms allow plants to cope with adverse surroundings as well as to synchronise themselves with predictable changes such as the change from day to night. Web We describe clock components sequentially expressed during a 24-h day that regulate rhythmic growth aging immune response and resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses.
These natural processes respond primarily to light and dark and affect most living things including animals plants and microbes. Web Circadian hormonal and sleep rhythm disruptions are commonly experienced concerns among cancer patients throughout the cancer care continuum. The plant circadian clock is a complex network of intertwined feedback loops comprised of repressor and activator transcription factors Harmer 2009.
The circadian rhythm of an organism depends on their surrounding environment. Web The circadian clock allows perception and anticipation of daily and seasonal changes resulting from the earths rotation. The molecular mechanisms of circadian clock regulation evolved independently several times testimony to its importance Nohales and Kay 2016.
We also discuss the role of the clock in the adaptation of crop species to different latitudes and to distinct biotic and abiotic stresses. In this study a link is made between plant immune responses and the circadian clock. Circadian rhythms are observable biological oscillations that occur with a 24-hour periodicity.
Web Nearly a century passed before period length of these leaf movements was accurately measured and it was realized that these rhythms were only 24 h making the rhythms circadian and suggesting that these rhythms were endogenous and not simply responses to environmental time cues. The Focus Issue was published in October 2022. 103389fpls2022836244 Abstract Plants require an endogenous regulatory network and mechanism to cope with diurnal environmental changes and compensate for their sessile nature.
The circadian oscillator is a complex network of interconnected feedback loops that regulates a wide range of physiological processes. Web The circadian clock a time-keeping mechanism drives nearly 24-h self-sustaining rhythms at the physiological cellular and molecular levels keeping them synchronized with the cyclic changes of environmental signals. Web THE PLANT CIRCADIAN CLOCK.
Web Circadian rhythms regulate a wide variety of developmental and metabolic processes resulting in enhanced fitness. A circadian network has 3 properties. Although plants have provided many examples of rhythmic outputs and our understanding of photoreceptors of circadian input pathways is well advanced studies with plants have lagged in the identificat.
Levelsoftheseproteinsare in constant flux each peaking at a specific time of day and.

Circadian Rhythms How Do Plants Keep Time

Circadian Rhythms How Do Plants Keep Time

Circadian Rhythm And Biological Clock

Role Of Circadian Rhythm In Plant System An Update From Development To Stress Response Sciencedirect

Csiro Publishing Functional Plant Biology

Environment Mediated Mutagenetic Interference On Genetic Stabilization And Circadian Rhythm In Plants Springerlink

Thermal Adaptation And Plasticity Of The Plant Circadian Clock Gil 2019 New Phytologist Wiley Online Library
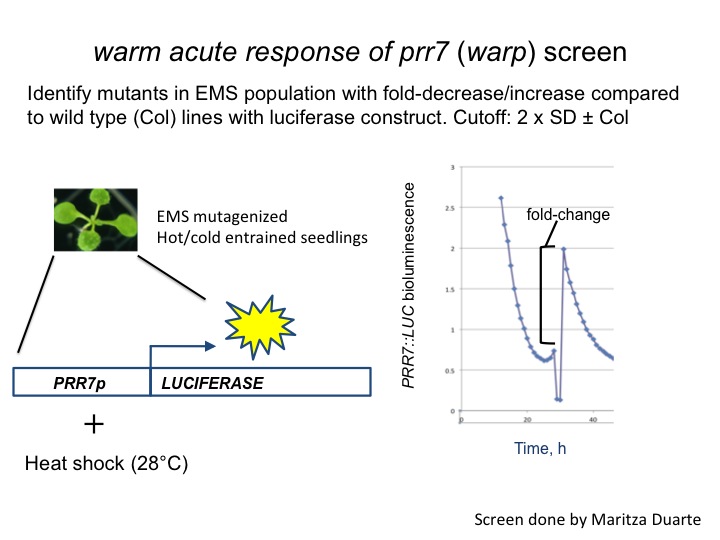
Temperature And The Circadian Clock Harmon Lab
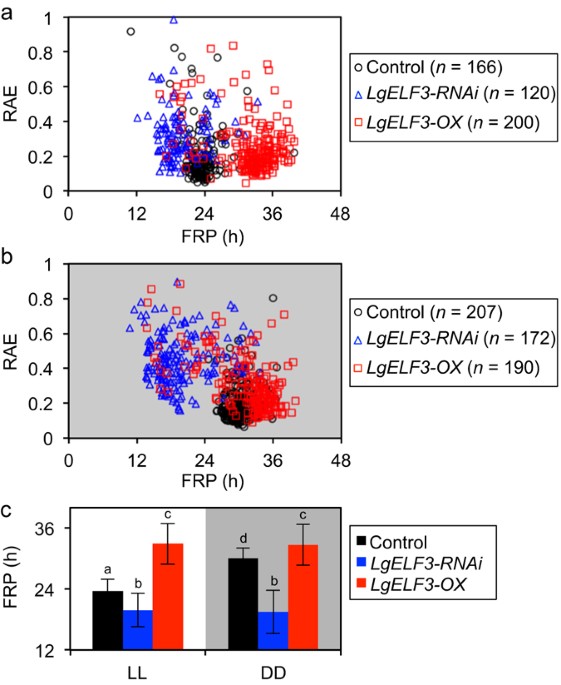
Synchrony Of Plant Cellular Circadian Clocks With Heterogeneous Properties Under Light Dark Cycles Scientific Reports

Circadian Rhythm And Biological Clock

Circadian Clock In Plants Linking Timing To Fitness Xu 2022 Journal Of Integrative Plant Biology Wiley Online Library

Circadian Rhythm And Biological Clock

The Circadian Clock Sets The Pace Of Plant Growth
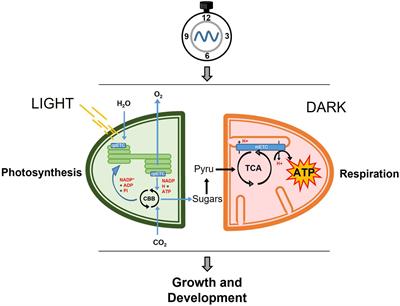
Plant Circadian Rhythms Frontiers Research Topic
Circadian Rhythms In Plants Latest Research And News Nature
Circadian Rhythms In Plants Latest Research And News Nature

Role Of Circadian Rhythm In Plant System An Update From Development To Stress Response Sciencedirect